Dental implants are advanced, long-lasting solutions for replacing missing teeth. They are designed to look, feel, and function just like natural teeth, making them one of the most popular options in modern restorative dentistry. Unlike dentures or bridges, which rest on the gums or rely on adjacent teeth for support, dental implants are surgically placed into the jawbone, providing a stable and permanent foundation for artificial teeth.
What Are Dental Implants?
A dental implant is a small, screw-like post—usually made from titanium or zirconia—that acts as an artificial tooth root. This post is surgically inserted into the jawbone where a tooth is missing. Over time, the implant fuses with the surrounding bone through a natural process called osseointegration. This fusion provides strength and durability similar to that of a natural tooth root.
Once the implant has integrated with the bone, an abutment is attached to connect the implant post with the dental crown, which is the visible part of the artificial tooth. The crown is custom-made to match the color, shape, and size of your natural teeth, ensuring a seamless and aesthetic appearance.
The Dental Implant Procedure
The process of getting dental implants typically involves several stages and can take a few months to complete, depending on individual healing times and treatment complexity.
Consultation and Planning:
The dentist or oral surgeon evaluates the patient’s oral health, takes X-rays or 3D scans, and determines bone density. A personalized treatment plan is then created.
Implant Placement Surgery:
During a minor surgical procedure, the implant post is inserted into the jawbone. Local anesthesia or sedation is used to ensure comfort throughout the process.
Healing and Osseointegration:
The bone gradually heals around the implant, forming a secure bond. This stage usually takes between three to six months.
Abutment Placement:
After healing, a small connector called an abutment is attached to the implant post.
Crown Placement:
Finally, a custom-made crown is placed on top of the abutment, completing the restoration.
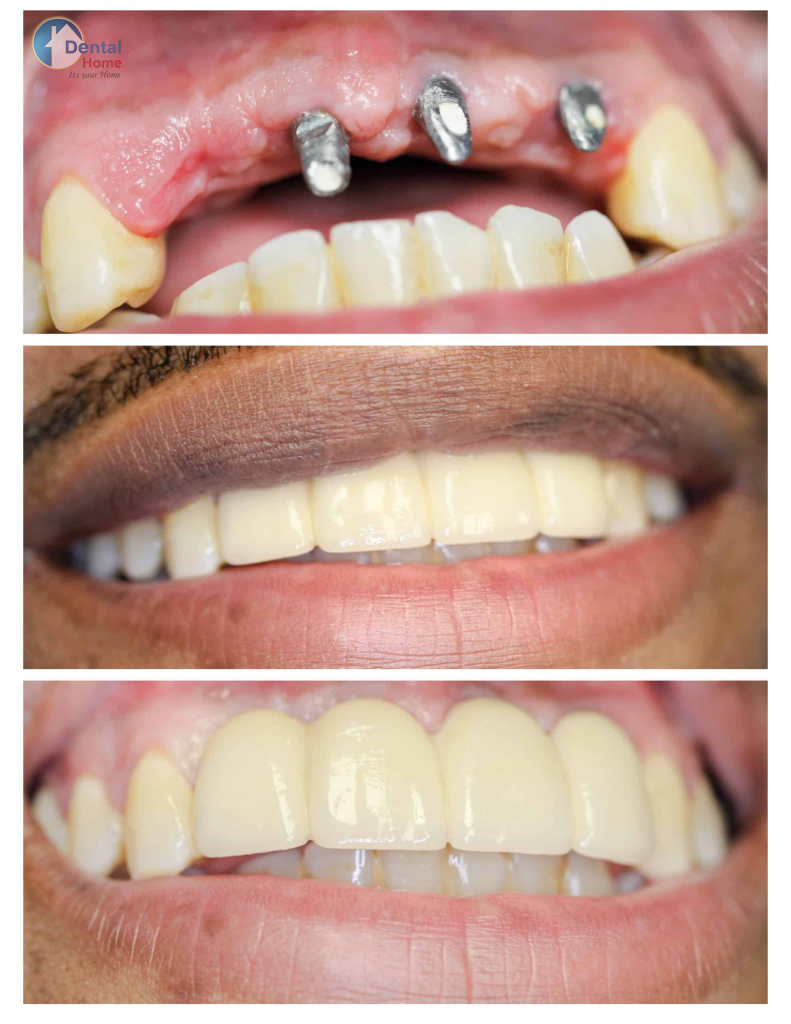
Types of Dental Implants
There are several types of dental implants available, depending on the patient’s needs and bone structure:
Endosteal Implants: The most common type, placed directly into the jawbone.
Subperiosteal Implants: Placed under the gum but above the jawbone, used when bone height is insufficient.
All-on-4 Implants: A modern technique where four implants support a full arch of teeth, ideal for patients missing most or all of their teeth.
Benefits of Dental Implants
Dental implants offer numerous advantages over traditional tooth replacement options:
Natural Appearance and Comfort: Implants blend seamlessly with natural teeth and feel comfortable in the mouth.
Improved Functionality: They restore normal chewing and speaking abilities without the slipping or discomfort often associated with dentures.
Bone Preservation: By stimulating the jawbone, implants help prevent bone loss that occurs after tooth extraction.
Durability: With proper care, dental implants can last for decades, making them a cost-effective long-term solution.
Enhanced Oral Health: Implants do not require the alteration of adjacent teeth, preserving natural tooth structure.
Maintenance and Care
Caring for dental implants is similar to maintaining natural teeth. Regular brushing, flossing, and dental check-ups are essential to keep the surrounding gums healthy and the implant free from plaque buildup. Avoiding smoking and maintaining good oral hygiene will extend the lifespan of the implants significantly.
Conclusion
Dental implants represent a remarkable advancement in dental technology, offering a permanent, comfortable, and natural-looking solution for tooth loss. They restore confidence, enhance oral function, and promote long-term dental health. For individuals seeking a reliable and aesthetic replacement for missing teeth, dental implants remain the gold standard of modern restorative dentistry.