Paediatric tooth treatment refers to the diagnosis, prevention, and management of dental issues in children, from infancy through adolescence. Because children’s teeth and jaws are still developing, their dental care requires specialized techniques, equipment, and a gentle, reassuring approach to ensure both oral health and a positive experience. Paediatric dentistry not only focuses on immediate treatment but also lays the foundation for lifelong healthy habits.
Goals of Paediatric Tooth Treatment
The primary objectives of paediatric dental care are:
- Preventing decay and gum disease through education, regular check-ups, and preventive treatments.
- Restoring damaged teeth to maintain function and appearance.
- Guiding proper jaw and tooth development to prevent long-term orthodontic issues.
- Managing dental emergencies in a child-friendly way.
Unlike adult treatment, paediatric dental care is as much about behavior management as it is about the actual procedure, ensuring that children feel safe and comfortable.
Common Paediatric Dental Problems
Children’s teeth are prone to specific conditions due to diet, habits, and developmental factors. These include:
- Early Childhood Caries (ECC): Rapid tooth decay caused by frequent sugary drinks, chocolates, or prolonged bottle use.
- Tooth fractures: Often the result of falls or sports injuries.
- Malocclusion: Misaligned teeth or jaws due to genetics, habits like thumb-sucking, or premature tooth loss.
- Eruption problems: Delays or abnormalities in how teeth come in.
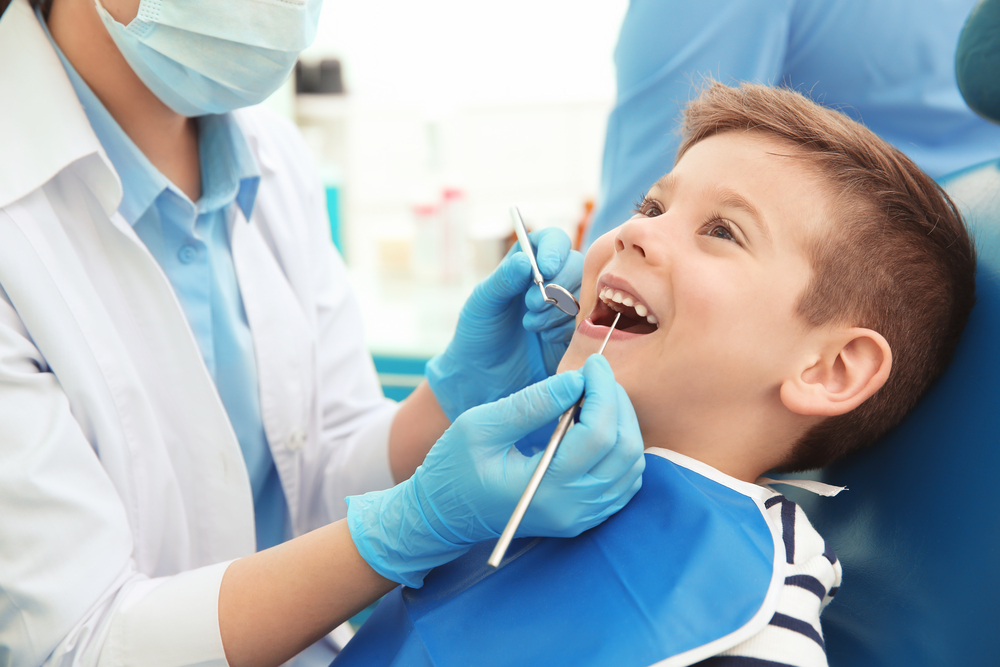

Types of Paediatric Tooth Treatments
a. Preventive Treatments
- Fluoride Applications: Strengthen tooth enamel and resist decay.
- Dental Sealants: Thin coatings placed on molar surfaces to block bacteria and food from settling in grooves.
- Professional Cleanings: Remove plaque and tartar buildup to prevent cavities and gum issues.
- Dietary Counseling: Advice on reducing sugary snacks and improving nutrition for oral health.
b. Restorative Treatments
- Tooth-Colored Fillings: Repair small to moderate cavities while maintaining a natural look.
- Porcelain Crowns: Durable caps for severely decayed primary teeth to maintain chewing function and space for permanent teeth.
- Pulp Therapy (Pulpotomy/Pulpectomy): It is the partial or total removal of the pulp, like root canal treatment for children, used when decay or injury affects the tooth’s pulp.
c. Orthodontic Interventions
- Space Maintainers: Keep space open if a baby tooth is lost early, preventing future crowding.
- Early Orthodontic Appliances: Help correct developing bite issues before they worsen.
d. Emergency Care
- Treating knocked-out or fractured teeth promptly to save them or restore appearance and function.
4. Behavior Management in Paediatric Dentistry
Children often feel anxious about dental visits. Paediatric dentists use strategies such as:
- Tell-Show-Do: Explaining and demonstrating before performing a procedure.
- Positive Reinforcement: Praising cooperation to encourage good behavior.
- Distraction Techniques: Using stories, videos, or music in a colourful, decorated room.
- Sedation or General Anesthesia: Sedation procedure may be needed for extensive treatment or high anxiety, performed with strict safety protocols.
Importance of Early Dental Care
The American Academy of Paediatric Dentistry recommends a first dental visit by age one. Early intervention can:
- Detect problems before they become severe.
- Reduce treatment costs by preventing complex issues.
- Build trust between the child and dentist, making future visits easier.
Neglecting primary teeth because they are “temporary” is a common misconception. Healthy primary teeth are equally important for speech development, nutrition, and guiding the permanent teeth into the correct position.
Role of Parents in Paediatric Tooth Treatment
Parents play a crucial role by:
- Supervising daily brushing and flossing until the child develops proper skills.
- Providing a balanced diet low in added sugars.
- Scheduling regular dental check-ups.
- Setting a positive example by practicing good oral hygiene themselves.
Conclusion
Treatment of the primary or baby tooth is about more than fixing cavities—it’s about establishing a lifetime of healthy oral habits. By combining preventive measures, early treatment, and a supportive environment, paediatric dentists help children grow into adults with strong, healthy smiles. Early, consistent care ensures not only healthy teeth and gums but also a confident, positive attitude toward dental health for years to come.